Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire, the top world cocoa producers, through a joint initiative have convinced chocolate traders and makers to increase the price they pay for cocoa.
These cocoa producing countries suspended the forward sales of cocoa beans which had a negative impact on global prices that, in less than a month, chocolate traders and makers agreed to the idea of a $400 a tonne premium on all cocoa sales contracts.
The joint initiative, known as the “living income differential” (LID), will take effect in the 2020-2021 season, which begins in October.
This follows reports of these countries earning less than they invest.
According to reports, ECOWAS member countries account for 68% of global cocoa supply. In the 2019-2020 season, they produced 3.4 million tonnes out of a worldwide total of 5 million tonnes.
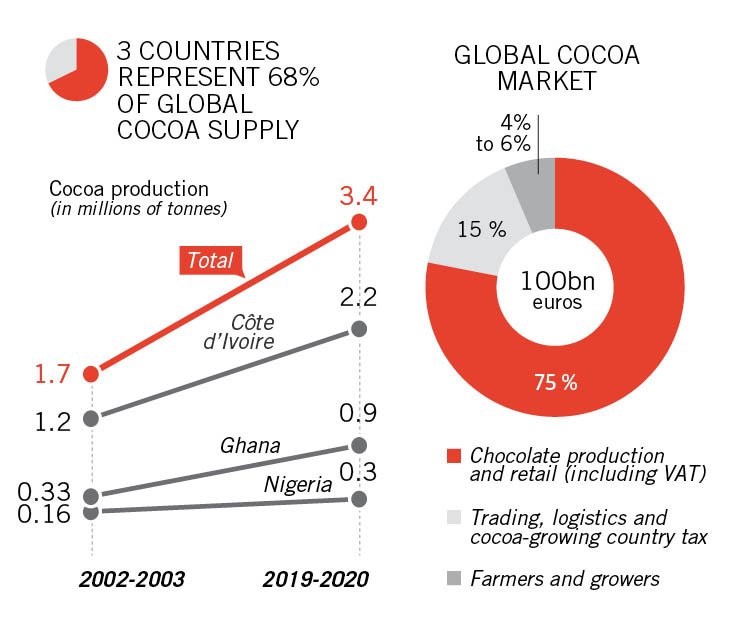
However, figures from the International Cocoa Organisation (ICCO) show that these countries capture just three percent of global chocolate.
Although Côte d’Ivoire produced 2.1 million tonnes of cocoa in 2017 (44% of global output), it brought in just $3.3billion (€2.9billion) from the trade, compared to earnings of $22billion for US chocolate majors.
Meanwhile, processes have been put into place to address the situation.
On 26 March 2018, cocoa farmers and trade federations from Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana formed their first strategic partnership agreement. In July 2019, Côte d’Ivoire’s Coffee and Cocoa Board (CCC) and the Ghana Cocoa Board (COCOBOD) successfully imposed a pricing mechanism to help producers earn a living wage.
This move will help ensure better pay to producers, coordinate production seasons and set a standard price for producers to prevent smuggling along the border.

